Il 23 And Il 17
Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics
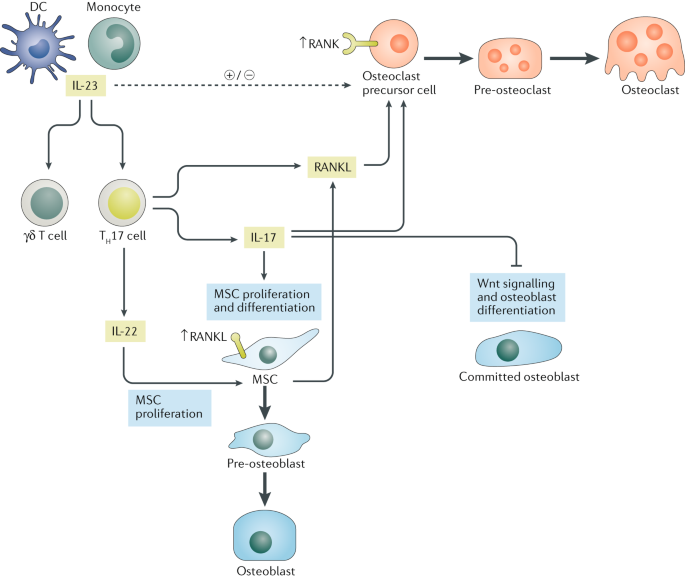
Effects Of The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway On Bone In Spondyloarthritis Nature Reviews Rheumatology

Il 23 Interleukin 23 Producing Conventional Dendritic Cells Control The Detrimental Il 17 Interleukin 17 Response In Stroke Stroke

Th17 Cells Inflammation And Regulation
Expression Of Il 23 Th17 Related Cytokines In Basal Cell Carcinoma And In The Response To Medical Treatments

Roles Of Interleukin 17 In Uveitis Guedes Mc Borrego Lm Proenca Rd Indian J Ophthalmol
The Th17/Treg Cells and IL-23/IL-17 Axis and Early Enteral Nutrition in Sepsis The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators.
Il 23 and il 17. 27, 28 The first report on IL-17 in IBD came from a study showing that the inflamed gut of patients with CD and patients with UC contains high levels of IL-17. Carinii-infected C57BL/6 mice were lightly anesthetized with ketamine-xylazine at day 5 after P. Morphine treatment disrupts the IL-23/IL-17 axis, leading to diminished host release of antimicrobial proteins S100A8/.
IL-17 inhibition has shown good efficacy in clinical trials for ankylosing. Understanding the IL-23–IL-17 immune pathway Interleukin (IL)-23 is a heterodimeric cytokine closely related to IL-12. Leveraging these promising therapeutic targets has led to the emergence of a number of anti‐IL‐23 and ‐17 biologic agents with the potential to treat multiple conditions.
Ab was administered twice a week for up to 4 weeks afterwards. The IL-23/IL-17 axis plays an important role in the development of chronic inflammation and in host defenses against bacterial infection. T1 - IL-23/IL-17 biology and therapeutic considerations.
(A) In chronic inflammation, antigen-stimulated dendritic cells and macrophages produce IL-23, which promotes the development of Th17/ThIL-17cells. In this application we will use transgenic mice to dissect IL-23 from the IL-23/IL-17 axis and more importantly from its effects on lymphoid cell populations. IL-17-producing γδ T cells to SpA pathogenesis is certainly not an open-and-shut case.
IL17A (Interleukin 17A) is a Protein Coding gene. Yet, despite a strong structural relationship that includes a shared p40 subunit, this does not translate into functional similarity. Who isolated IL17 transcript from a rodent T-cell hybridoma.
IL-23 induces the earliest recruitment of neutrophils to the site of infection and promotes the development and maintenance of Th17 cells. IL-23 enhances the expansion of IL-22–producing cells during Th17 differentiation. If the IL-23–IL-17 immune pathway becomes dysregulated, there is a danger of breaking tolerance to ‘self’ tissues and antigens, leading to severe autoimmune pathologies such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and Crohn's disease, which severely debilitate millions of sufferers.
The crucial role of the IL-23/IL-17 pathway in the early recruitment of large numbers of neutrophils in mucosal and non-mucosal tissues via several cytokines and chemokines has been well documented. Indeed, the cell types that are chiefly involved in local inflammation in human SpA still remain largely unclear. IL-23 is among a group of cytokines that activate signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-3.
Under physiological conditions, Th17 cells and IL-23-producing cells are enriched in the gut mucosa, and differentiation of Th17 cells is mostly modulated by intestinal microbiota. On the one hand, IL-17 deficient or anti-IL-17 treated mice exhibited severe epithelial damage in the colon, indicating a protective function of IL-17 133. Carinii inoculation and 1 μg of neutralizing anti-murine IL-17 Ab (R&D Systems) was given to each mouse intranasally.
Interleukin 23 is a heterodimeric cytokine composed of two subunits:. The involvement of IL-23 and IL-17 in IBD is well documented;. IL-23 is known to activate myeloid and lymphoid cells and thus plays a critical pathogenic role in PsA.
IL-17 and IL-23 neutralization. The IL‐17 inhibitors were overall shown to have a higher efficacy than the IL‐23 inhibitors during induction therapy. IL-23 binds to its.
N2 - CD4+ T-lymphocytes are pivotal in immune responses to pathogens and in pathogenesis of various inflammatory diseases. The newest biologics for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis are IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors with unprecedented efficacy of complete skin clearance compared to older biologics. A critical target of IL-23 is a unique subset of tissue-homing memory T cells, which are specifically activated by IL-23 to produce the proinflammatory mediators IL-17 and IL-6.
To evaluate whether IL-17, IL-12/23 or TNF inhibitors are associated with an increased risk for serious infection in real-world patients with psoriasis or PsA, Li and colleagues conducted a. The discovery that the IL-23/IL-17 axis is of major importance for the pathogenesis of psoriasis has been confirmed by the efficacy of new therapeutics (1):. IL-23 stimulates the production of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF, IL-1β, and IL-17 from (a) Th17 cells, and IL-6 from (b) macrophages and DCs.
In mouse, IL-23 but not IL-12, has also been shown to induce memory T cells to secret IL-17, a potent proinflammatory cytokine. The cytokines IL-23 and IL-17 have an important role in the pathogenesis of, and as a therapeutic target in, both animal models of chronic inflammation and some human chronic inflammatory diseases. The robust investigation into IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors to treat plaque psoriasis has yielded promising results, including the unprecedented rates of PASI 100 achievement with these new biologics.
The relationship between IL-23 and IL-17 is known as the IL-23/IL-17 axis. However, the different functions of IL-17 in IBD are still controversially discussed in the literature 131,132. 5, 37 IL‐17 is also produced in γδ T cells and invariant natural killer T cells independently of IL‐23.
IL-23 has been shown to be a key cytokine for Th17 maintenance and expansion. Recently, we reported that tumor-derived lactic acid enhances the toll-like receptor. AU - Dong, Chen.
The Interleukin 23 (IL-23) cytokine is a heterodimeric cytokine consisting of the two subunits p19 and p40. Activation of gut T helper 17 (Th17) cells by interleukin (IL)-23 promotes chronic tissue inflammation, and the IL-23/IL-17 cytokine axis presumably plays a key role in the chronic gut inflammation associated with spondyloarthritis. The heterodimeric cytokine IL-23, which was secreted mainly by activated dendritic cells and macrophages in response to TLR activation, stimulate T-cell differentiation and function in linking innate and adaptive immunity.
This pathway may be responsible for chronic intestinal inflammation as well as other chronic autoimmune inflammatory diseases. It is an inducer of the Th17 cell population and a component of the IL-23/IL-17 immune pathway which is an orchestrator of many pathological conditions, including psoriasis. Risankizumab, guselkumab, and tildrakizumab are new IL-23 inhibitors currently in phase 3 trials with promising early efficacy and safety results.
However, the IL‐17 inhibitors had an increased risk of adverse events when compared to placebo, while there was no increased risk with any of the IL‐23 inhibitors. Our current findings indicate that activation of the IL-23/IL-17 axis may be important in driving an early immune response against S. IL-12 and IL-23 can induce IL-12 production from mouse splenic DC of both the CD8-and CD8 + subtypes, however only IL-23 can act directly on CD8 + DC to mediate immunogenic presentation of poorly immunogenic tumor/self.
(c) IL-17 interacts with IL-17RA/RC complex. Abstract IL-23 induces the differentiation of naive CD4 (+) T cells into highly pathogenic helper T cells (Th17/Th (IL-17)) that produce IL-17, IL-17F, IL-6, and TNF-alpha, but not IFN-gamma and IL-4. Il-23, identified as a heterodimeric proinflammatory cytokine, is a member of the IL-12 superfamily composed of a p40 subunit (shared with the IL-12 cytokine) and a unique p19 subunit;.
With regard to autoimmune diseases such as RA, ankylosing spondylitis, chronic inflammatory intestinal diseases, psoriasis, and MS, clinical research is. Secukinumab (Cosentyx), ixekizumab (Taltz), and brodalumab (Siliq) IL-12/IL-23 inhibitor:. Th17 are polarised by IL-6 and TGF-β which activate Th17 transcription factor RORγt.
Meanwhile, higher gene expression of IL-23, IL-17, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α was found in the tissues from LDH patients and a positive correlation between IL-17 and IL-23 gene expression was also observed. To further examine how IL-23 enhances IL-22 expression, we differentiated CFSE-labeled naive DO11 T cells to Th17 with various cytokines and analyzed the expression of IL-22 from days 1 to 5 of culture. Ustekinumab (Stelara) Doctors may also prescribe one or more of the following treatments:.
Methylated BSA (mBSA) and IL-23-induced neutrophil migration was inhibited by anti. It also enhances the development of Th17 mediated autoimmunity and tumor progression. P40, which is also a subunit of interleukin 12 and is targeted by ustekinumab (a biological drug approved for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis), and p19, which is expressed in interleukin 23 only.
The IL-23/IL-17 axis has a pivotal role in the complex pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases, which lead to the development of several therapeutics targeting different components within this pathway. This cytokine is produced by a group of T helper cell known as T helper 17 cell in response to their stimulation with IL-23. This results in decreased neutrophil recruitment and more-severe infection.
Taken all above results together, it may be deduced that higher expression of IL-23 may contribute to. IL-23 is important in the proliferation and maintenance of IL-17, and therefore, cytokines of the IL-23/IL-17 axis attracted much interest as therapeutic targets in psoriasis and PsA. Over the past decade, IL-23 has been identified as a key cytokine in human chronic.
Some studies focusing on blood or synovium from SpA patients reported augmented IL-17-producing and IL-23. IL-23 contributes to autoimmunity and host defense through IL-23 /IL-17–dependent pathways. IL-23/IL-17-induced neutrophil recruitment plays a pivotal role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
26, 27) to suppress the IL-23/IL-17 inflammatory axis in psoriasis and, furthermore, to provide evidence about how the combination of Cal and dexamethasone (Dex) effectively disrupt the positive cytokine feedback loop of IL-36 and IL-23/IL-17, which we believe underlies the superior efficacy of the combination therapy for psoriasis. Despite its role in inflammation, IL-17 is also required for the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Especially in the R group.
IL-23 receptor complex is composed of IL-23R subunit and the IL-12Rβ1 subunit (shared with the IL-12 receptor complex). Based on research results using GWAS and animal models, clinical trials have begun, targeting either IL-23, which contributes to the final differentiation and function acquisition of pathogenic Th17 cells, or RORγt, which is a master transcription factor for Th17 cells, or IL-17, which is an effector cytokine 74, 106 (Figure 2). Originally, Th17 was identified in 1993 by Rouvier et al.
Fumigatus readily elicits IL-23 and IL-17 production from the lungs after exposure. The traditional view is that a main source of IL-17 is T cells and that IL-17 production is under the control of IL-23. Although IL-23 is a critical driver of IL-17, recognition of nonredundant and independent functions of IL-23 and IL-17 has prompted the notion that dual inhibition of both IL-23 and IL-17 could offer even greater efficacy for treating autoimmune diseases relative to targeting either cytokine alone.
Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. IL-17 and IL-23 receptor expression are up-regulated in lupus-prone mouse-derived T cells Th17 cell population maintenance and expansion relies heavily on IL-23. IL-23 is a proinflammatory cytokine.
Many pharmaceutical companies have now developed antibodies against IL-23 or IL-17 that have been largely successful in clinicaltrials, but theyhave also presented some unexpected results as well. IL-23 signals through a receptor complex consisting of IL-12 R beta 1 and IL-23 R. The crucial role of the IL-23/IL-17 pathway in the early recruitment of large numbers of neutrophils in mucosal and nonmucosal tissues via several cytokines and chemokines has been well documented.
These discoveries include genetic association and the identification of IL-23- and IL-17-producing cells in the tissue of mouse models and human patients. Interleukin (IL)-17 plays a major role in the development of both psoriasis and PsA. This may partly.
Ment of IL-23 and IL-17 in autoimmune disorders has motivated the discovery of therapeutics for targeting IL-23 and IL-17 pathways. Here we report that prostaglandin enhances the IL-23/IL-17-induced neutrophil migration in a murine model of RA by inhibiting IL-12 and IFN γ production. Stimulation with IL-6, transforming growth factor-β , IL-21, IL-1β and IL-23 is required for differentiation of T h 17 cells and the production of IL-17A.
Interleukin 17A (IL-17 or IL-17A) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine. Diseases associated with IL17A include Arthritis and Bronchiolitis Obliterans.Among its related pathways are PEDF Induced Signaling and Immune response IL-23 signaling pathway.Gene Ontology (GO) annotations related to this gene include cytokine activity.An important paralog of this gene is IL17F. However, the mechanism of the neutrophil recruitment is obscure.
Over the past several years, genetic, experimental, and clinical studies have accumulated evidence showing that the IL-23/IL-17 axis plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of SpA. Advancements in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis have identified interleukin (IL)‐23 and IL‐17 as fundamental contributors in the immune pathways of the disease. In current pathogenic models of psoriasis, IL‐23 regulates Th17 cells, while IL‐17 is the downstream key effector cytokine mediating inflammation.
In 09, Ustekinumab (Stelara ®), a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the p40 subunit found in both IL-12 and IL-23, was approved for the treatment of psoriasis (75). Targeting IL-12/IL-23p40, as well as IL-23p19, seems efficacious and safe in the treatment of moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease in recent. Risankizumab, ixekizumab, and brodalumab have demonstrated superior efficacy in trials compared to ustekinumab.
Interleukin-17A (IL-17A) is a cytokine produced by T h 17 cells that plays an important role in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and cancer. For IL-17 neutralization experiments, P.

Yin And Yang Of Interleukin 17 In Host Immunity F1000research

The Interleukin Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Ankylosing Spondylitis New Advances And Potentials For Treatment Jethwa 16 Clinical Amp Experimental Immunology Wiley Online Library

Il 17 And Therapeutic Kynurenines In Pathogenic Inflammation To Fungi The Journal Of Immunology

Pro Inflammatory Th17 Cells And Glucocorticoid Resistance Implications For Chronic Inflammatory Diseases And Their Treatment Brainimmune Trends In Neuroendocrine Immunology Brainimmune Trends In Neuroendocrine Immunology

Distinct Roles Of Il 23 And Il 17 In The Development Of Psoriasis Like Lesions In A Mouse Model The Journal Of Immunology

Figure 1 From Pathogenic Role Of Il 17 In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis Semantic Scholar
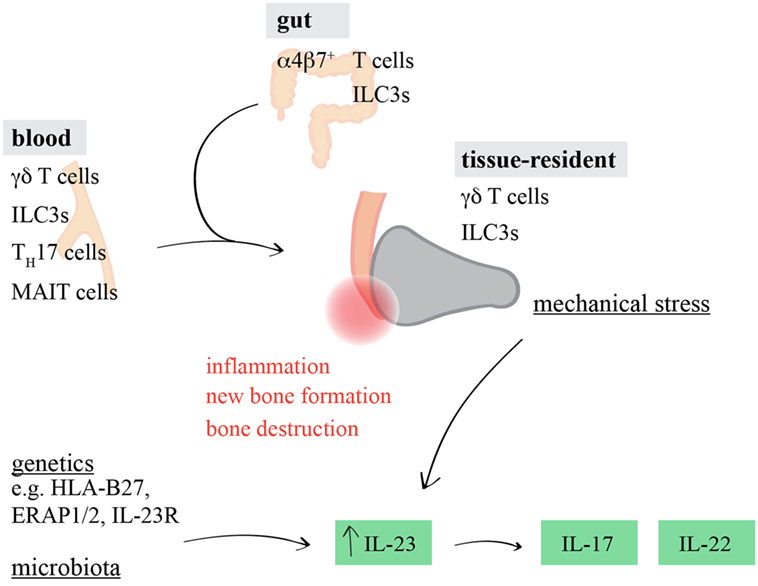
Frontiers Whodunit The Contribution Of Interleukin Il 17 Il 22 Producing Gd T Cells Ab T Cells And Innate Lymphoid Cells To The Pathogenesis Of Spondyloarthritis Immunology

Mechanism Of Action Moa Ilumya Tildrakizumab Asmn Hcp
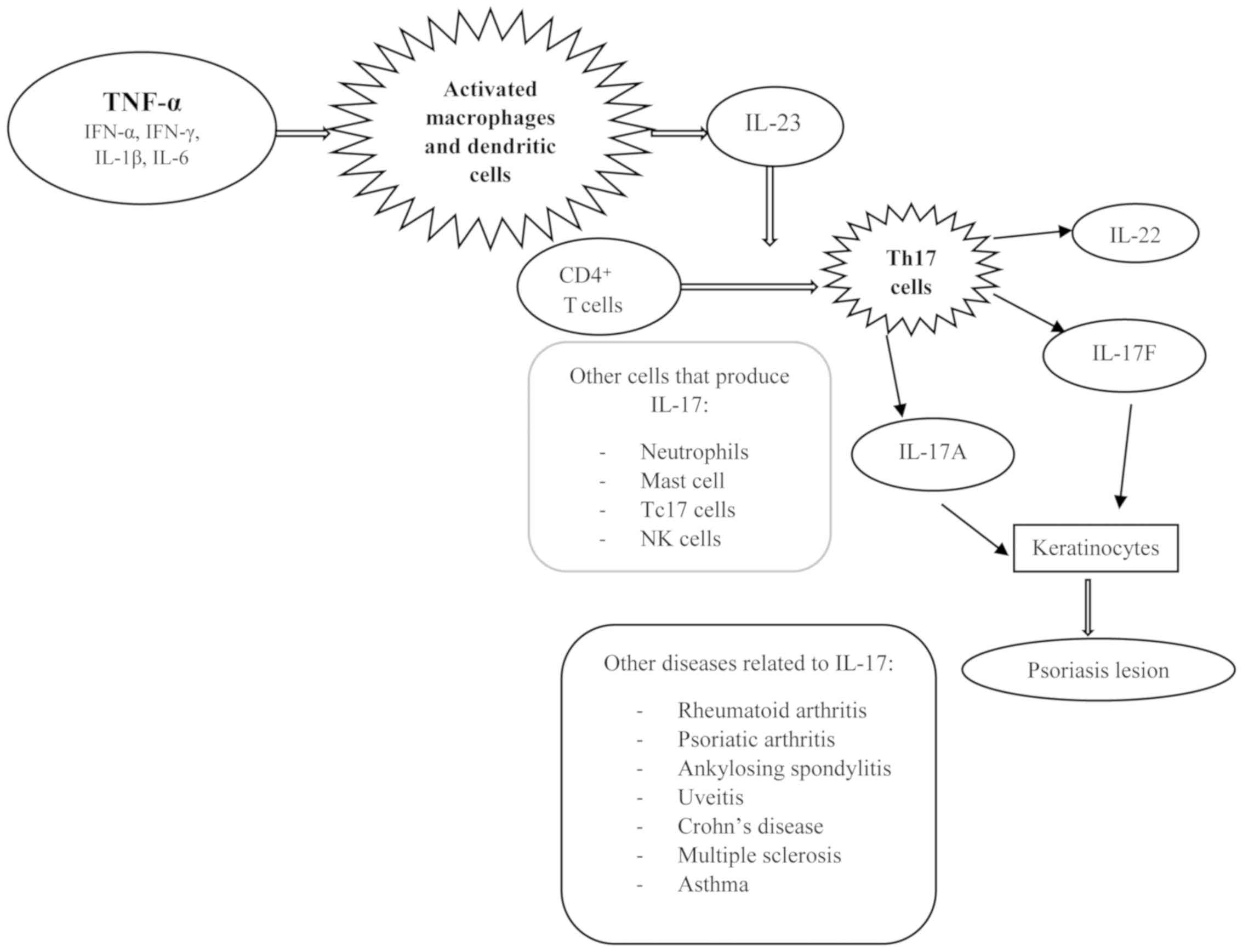
Psoriasis Association Of Interleukin 17 Gene Polymorphisms With Severity And Response To Treatment Review

Article Jddonline Journal Of Drugs In Dermatology

Interleukin 23 Inhibition As A Strategy To Treat Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases European Medical Journal

Why Did Il 23p19 Inhibition Fail In As A Tale Of Tissues Trials Or Translation Annals Of The Rheumatic Diseases

Interleukin 23 And Interleukin 17 Importance In Pathogenesis And Therapy Of Psoriasis

The Role Of Il 17 And Related Cytokines In Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases
1

Il 23 Interleukin 23 Producing Conventional Dendritic Cells Control The Detrimental Il 17 Interleukin 17 Response In Stroke Stroke
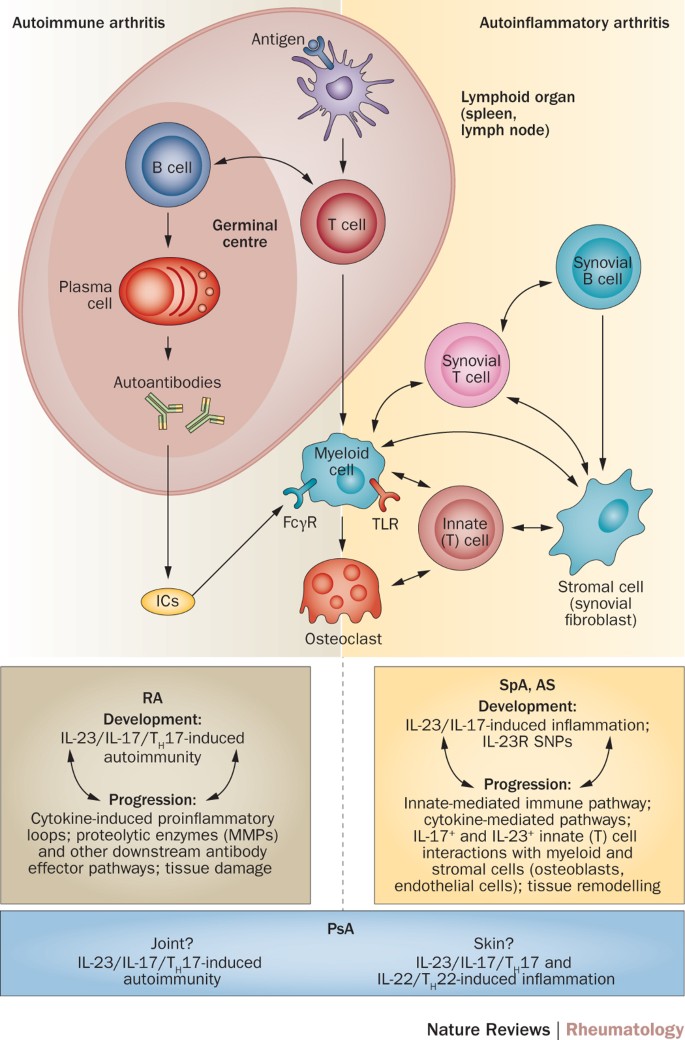
The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Inflammatory Arthritis Nature Reviews Rheumatology

Emerging Role Of Interleukins Il 23 Il 17 Axis And Biochemical Markers In The Pathogenesis Of Type 2 Diabetes Association With Age And Gender In Human Subjects Sciencedirect

The Cytokines Axis In Psoriasis Il 23 Il 17 Axis Related Mediators Download Scientific Diagram

Therapeutic Applications Strategies And Molecules Targeting The Il 17 Th17 Pathway Musculoskeletal Key

Innate Il 17 And Il 22 Responses To Enteric Bacterial Pathogens Trends In Immunology

Why Did Il 23p19 Inhibition Fail In As A Tale Of Tissues Trials Or Translation Annals Of The Rheumatic Diseases
Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177
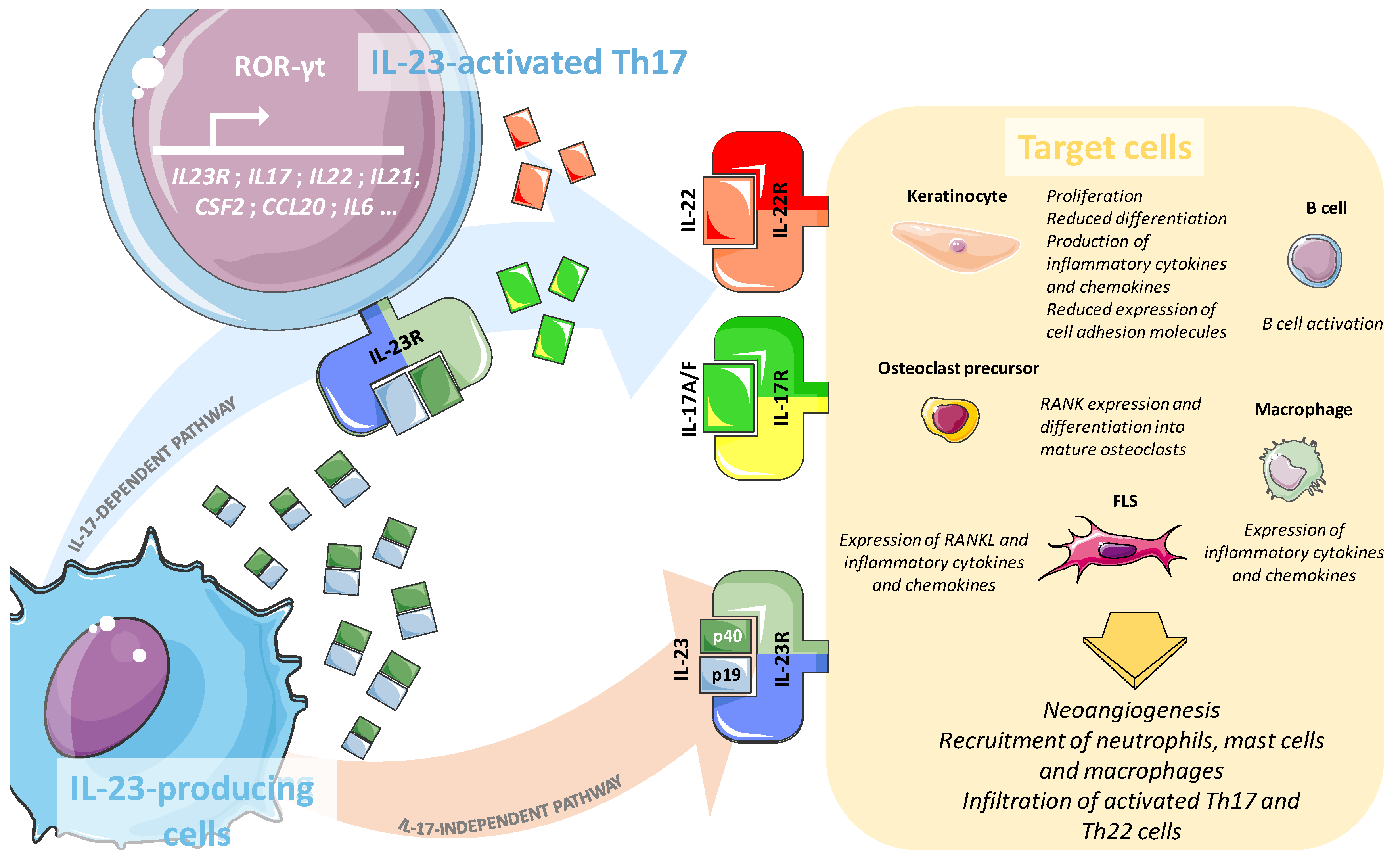
Ijms Free Full Text Role Of The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis The Clinical Importance Of Its Divergence In Skin And Joints Html

Role Of Interleukin 23 Il 23 Receptor Signaling For Il 17 Responses In Human Lyme Disease Infection And Immunity

Interleukin 17 Cytokine Signalling In Patients With Asthma European Respiratory Society
Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf

Jci Insight Disrupting The Il 36 And Il 23 Il 17 Loop Underlies The Efficacy Of Calcipotriol And Corticosteroid Therapy For Psoriasis

T Helper 17 Cells In Psoriatic Plaques And Additional Genetic Links Between Il 23 And Psoriasis Sciencedirect

Pdf Shifting The Focus The Primary Role Of Il 23 In Psoriasis And Other Inflammatory Disorders
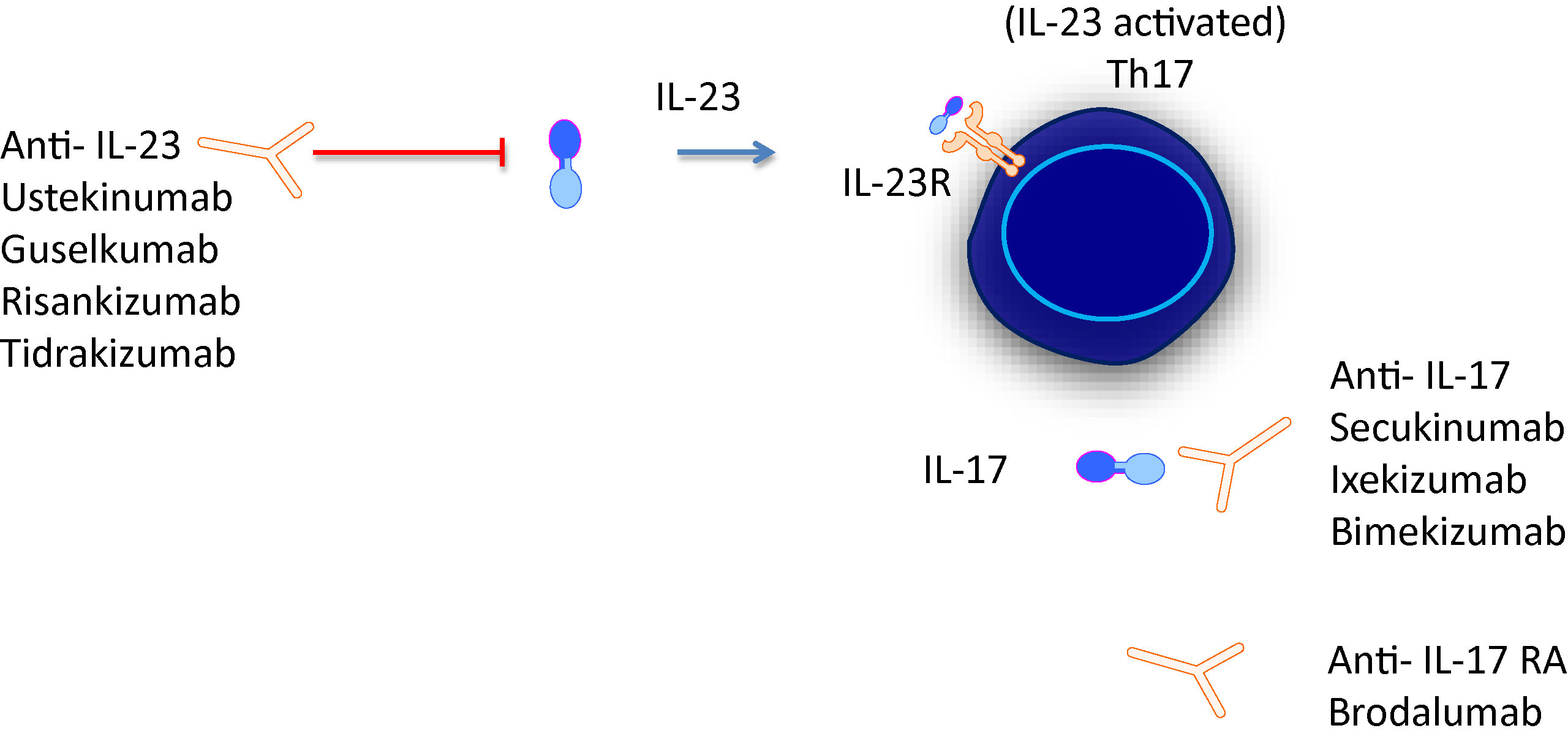
Frontiers Mini Review New Treatments In Psoriatic Arthritis Focus On The Il 23 17 Axis Pharmacology
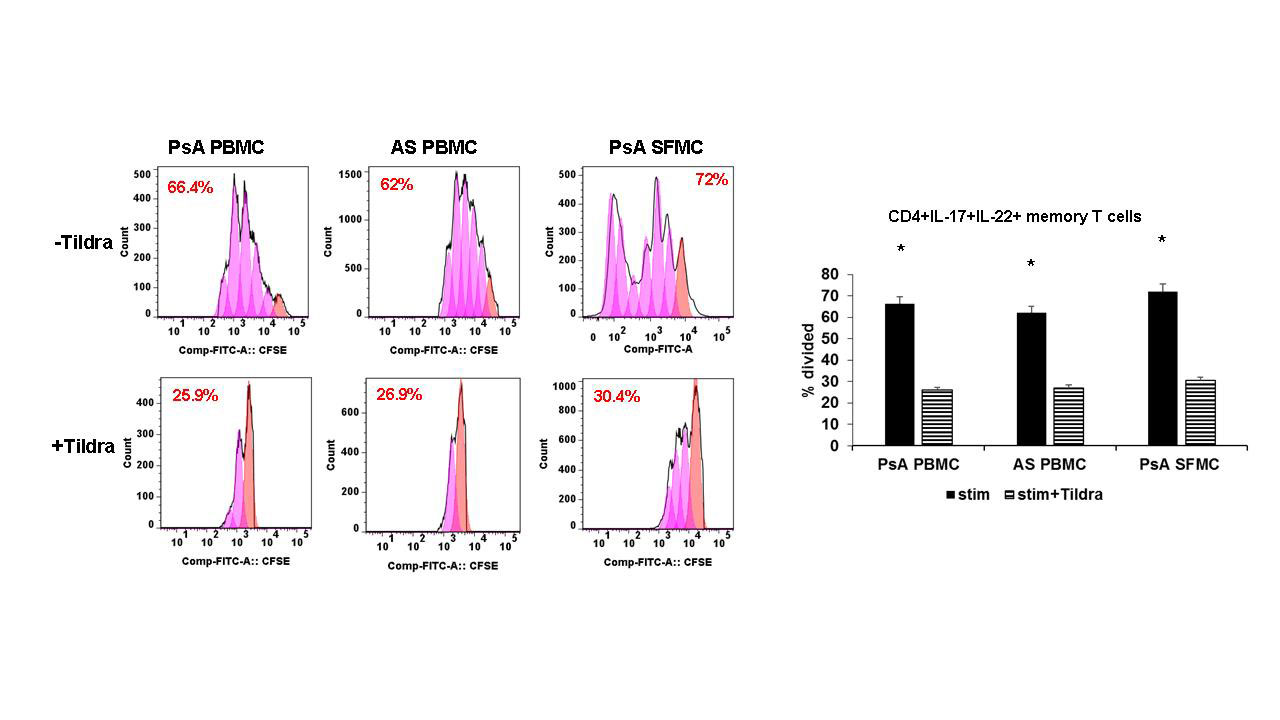
Regulatory Role Of Il 23 And Its Receptor System In Spondyloarthritis And Its Therapeutic Relevance In Anti Il 17 Failure Patients Acr Meeting Abstracts
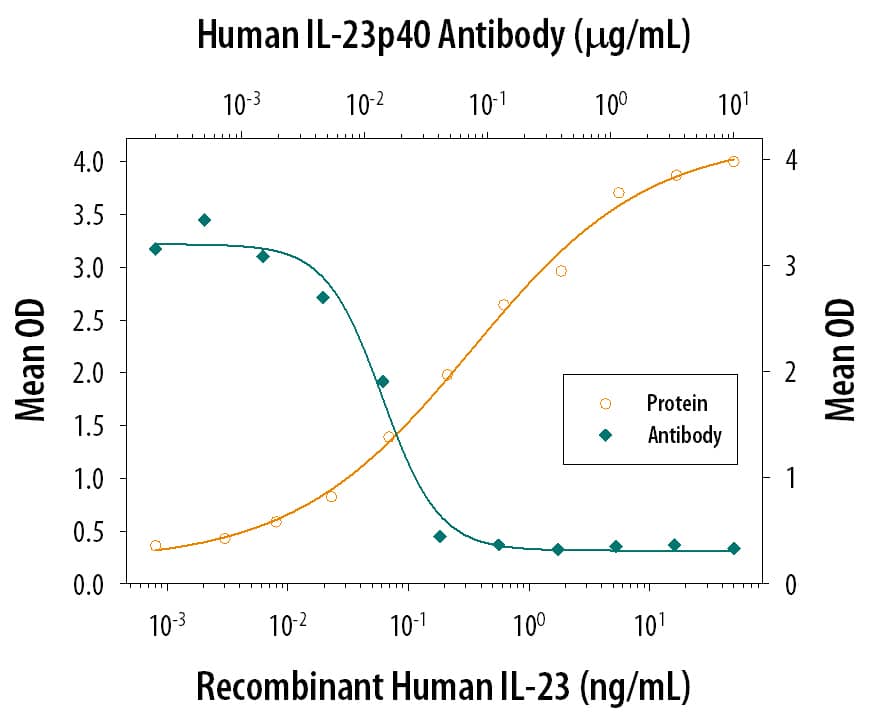
Human Il 12 Il 23 P40 Antibody Af309 R D Systems
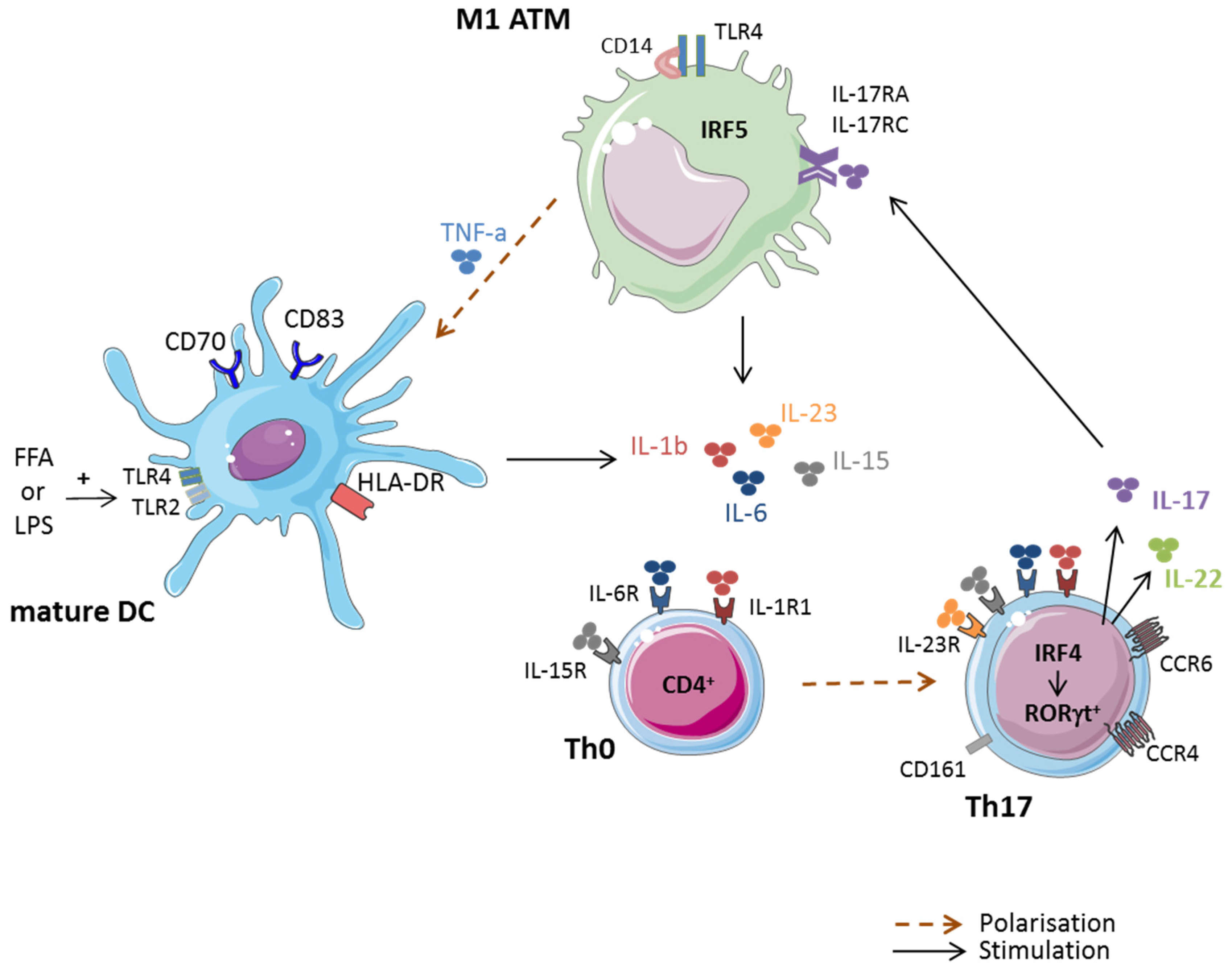
Jcm Free Full Text Pathogenic Role Of Il 17 Producing Immune Cells In Obesity And Related Inflammatory Diseases Html
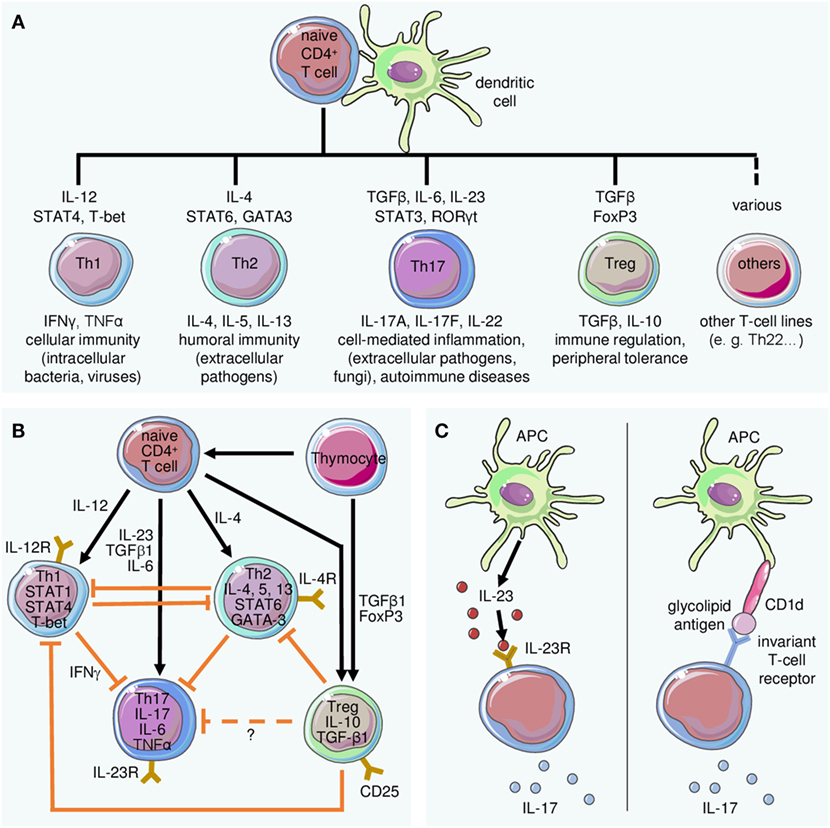
Frontiers The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis Links Adaptive And Innate Immunity In Psoriasis Immunology

Jci The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Inflammation

Innate Il 17 And Il 22 Responses To Enteric Bacterial Pathogens Trends In Immunology
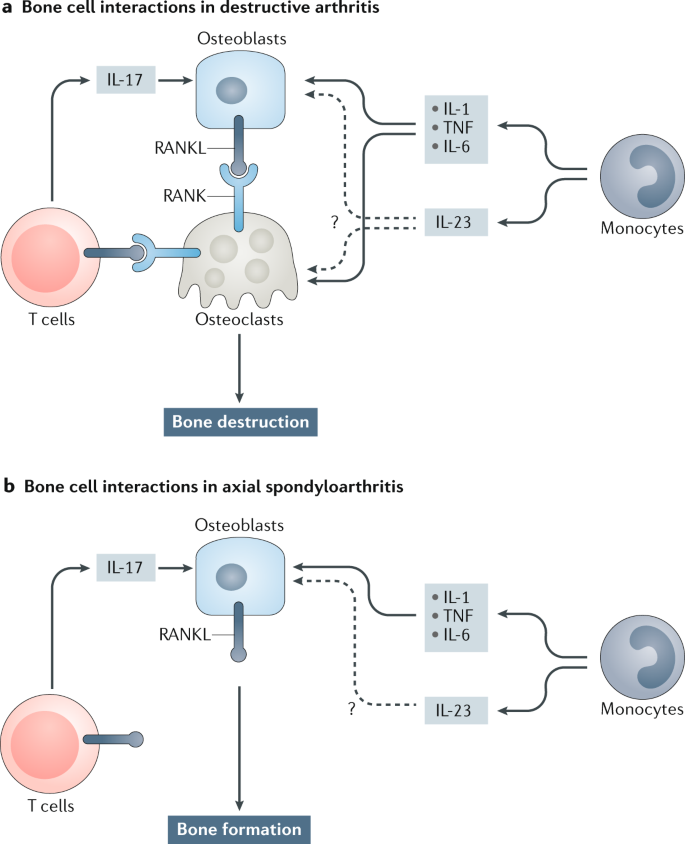
The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway As A Therapeutic Target In Axial Spondyloarthritis Nature Reviews Rheumatology
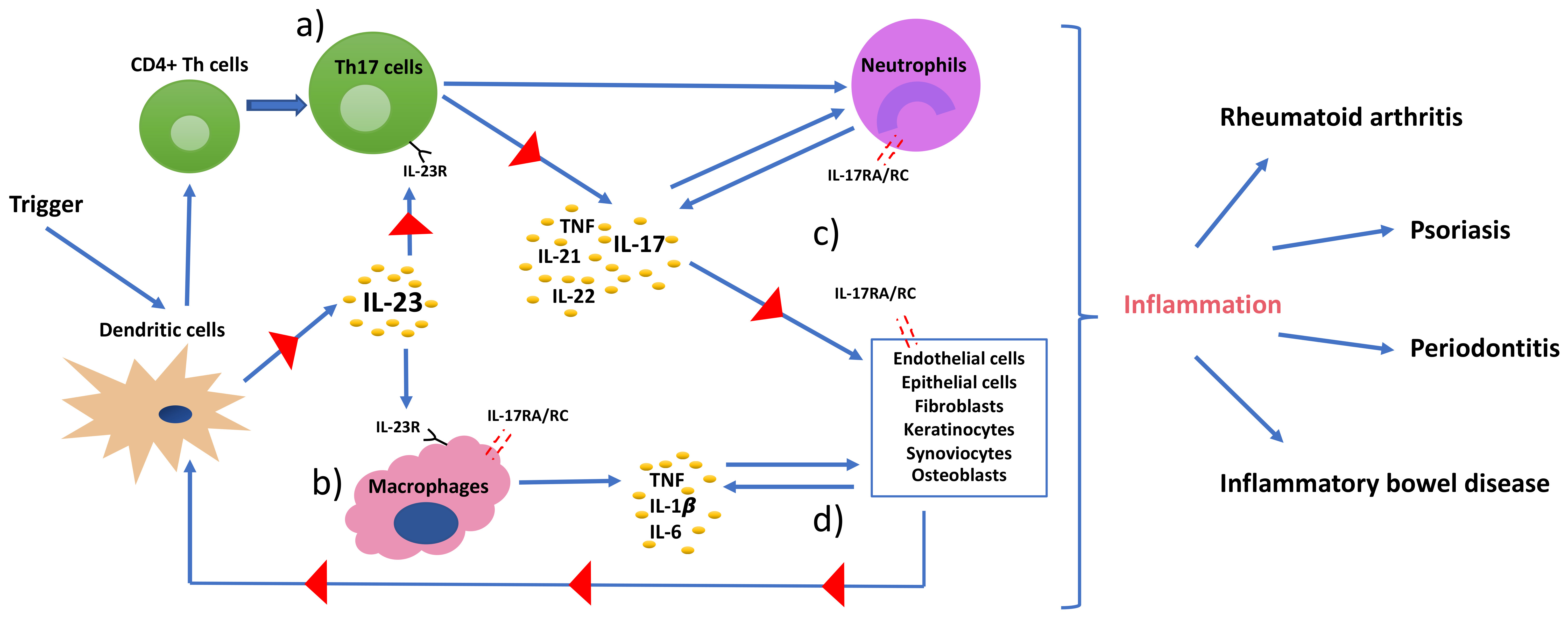
Ijms Free Full Text Th17 Cells And The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In The Pathogenesis Of Periodontitis And Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Html

The Protective And Pathogenic Roles Of Il 17 In Viral Infections Friend Or Foe Open Biology
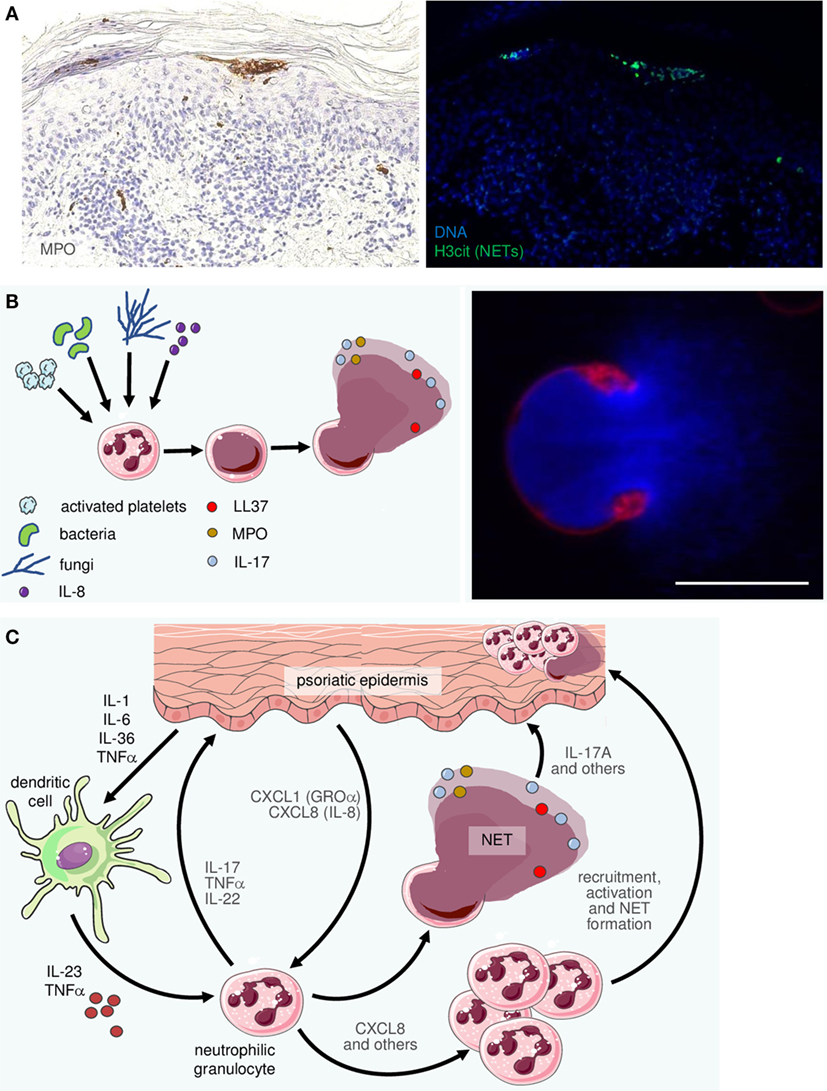
Frontiers The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis Links Adaptive And Innate Immunity In Psoriasis Immunology
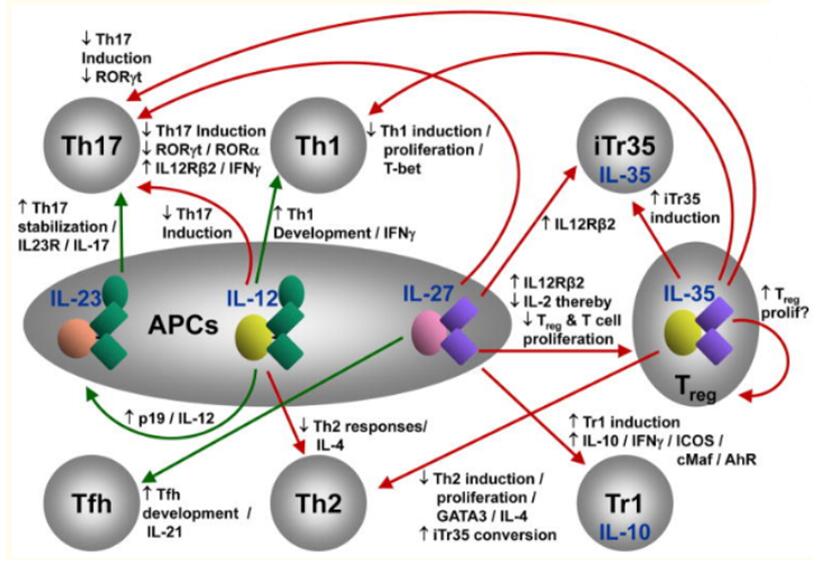
Il 12 Family Creative Diagnostics

The Role Of Il 23 And The Il 23 Th17 Immune Axis In The Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Psoriasis Girolomoni 17 Journal Of The European Academy Of Dermatology And Venereology Wiley Online Library
Plos One Expression Of Il 23 Th17 Related Cytokines In Basal Cell Carcinoma And In The Response To Medical Treatments

Il 23 Sugarcone Biotech

Pdf The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriatic Arthritis Semantic Scholar

Prostaglandin Mediates Il 23 Il 17 Induced Neutrophil Migration In Inflammation By Inhibiting Il 12 And Ifng Production Pnas
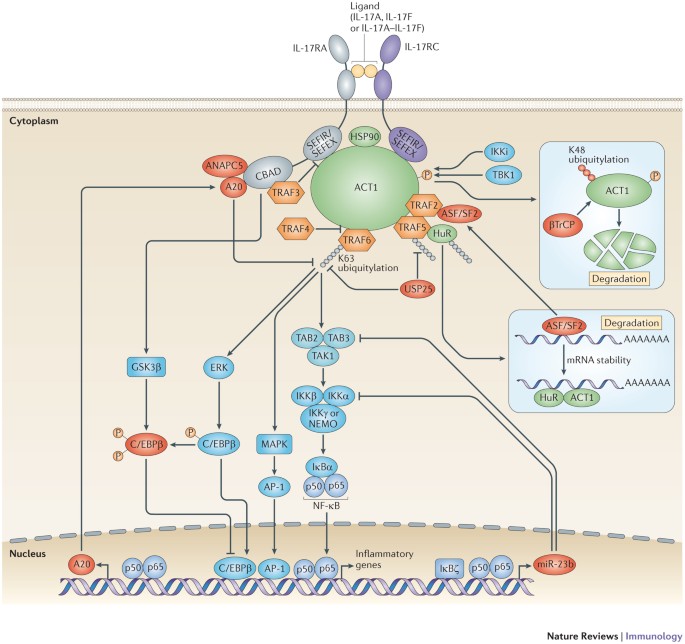
The Il 23 Il 17 Immune Axis From Mechanisms To Therapeutic Testing Nature Reviews Immunology
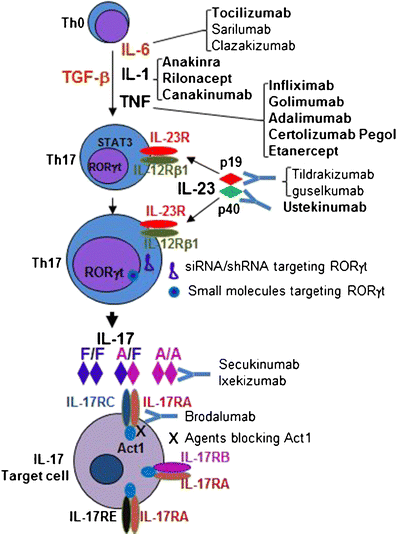
Figure 1 How Can We Manipulate The Il 23 Il 17 Axis Springerlink

Schematics Of Il 23 Il 17 Immune Axis Involved In The Pathogenesis Of Download Scientific Diagram
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrod4hu1vom2afleikd Mygmqwa8sipsohk4ykhbqio1ybsccmn Usqp Cau
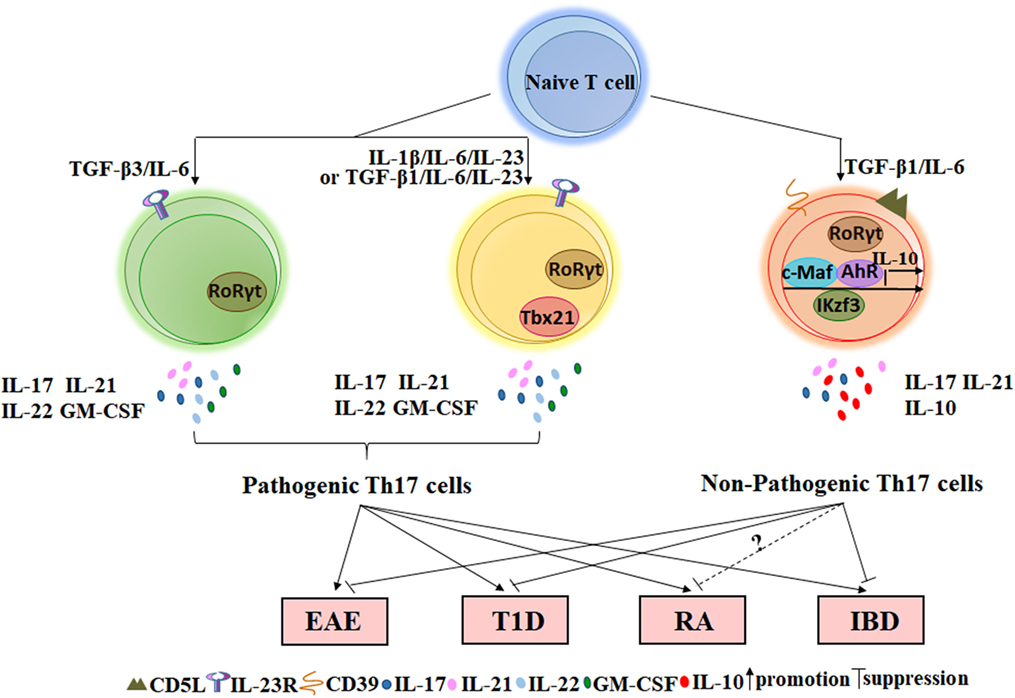
Frontiers Insight Into Non Pathogenic Th17 Cells In Autoimmune Diseases Immunology

Figure 1 From The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriatic Arthritis Semantic Scholar

Mouse Il 23 P19 Antibody Af1619 R D Systems

Dual Inhibition Of Interleukin 23 And Interleukin 17 Offers Superior Efficacy In Mouse Models Of Autoimmunity Journal Of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics
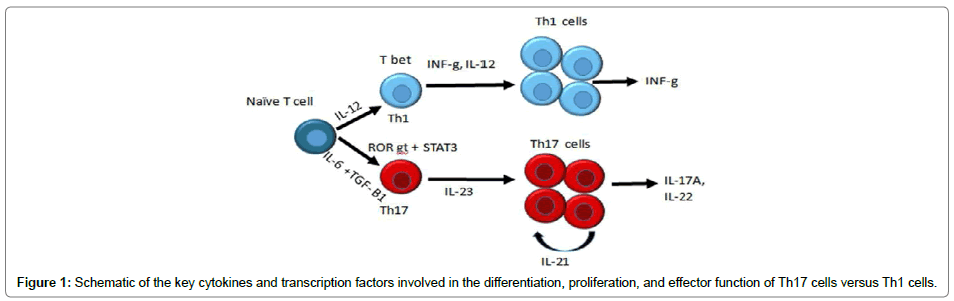
Il 17 Cytokine In Psoriasis Before And After Methotrexate And Nbuvb Phototherapy A Longitudinal Study Scitechnol

The Role Of Il 17a In Axial Spondyloarthritis And Psoriatic Arthritis Recent Advances And Controversies Annals Of The Rheumatic Diseases

Understanding The Il 23 Il 17 Immune Pathway Sciencedirect
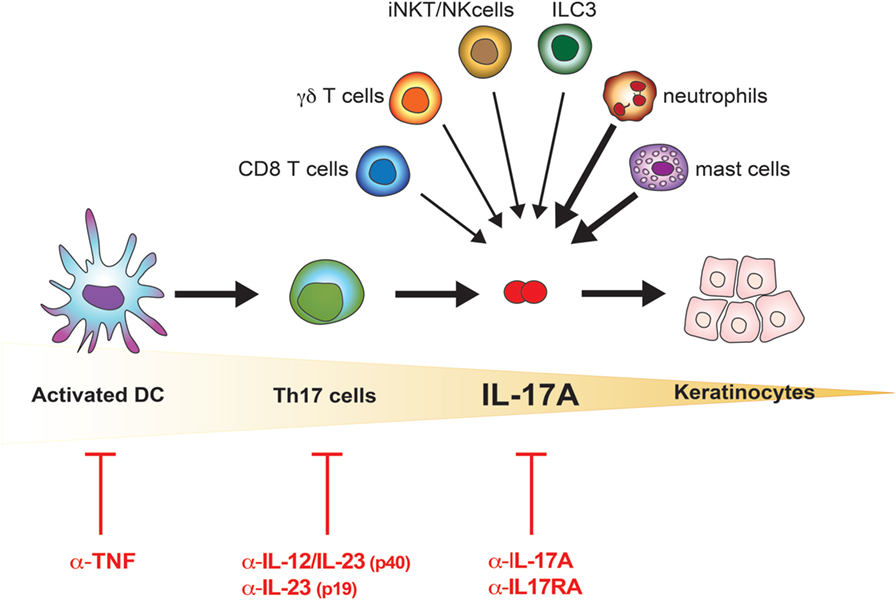
Frontiers The Il 17 Family Of Cytokines In Psoriasis Il 17a And Beyond Immunology

Psoriasis Pathogenesis And The Development Of Novel Targeted Immune Therapies Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Stat3 And Nf Kb Signal Pathway Is Required For Il 23 Mediated Il 17 Production In Spontaneous Arthritis Animal Model Il 1 Receptor Antagonist Deficient Mice The Journal Of Immunology

Dual Inhibition Of Interleukin 23 And Interleukin 17 Offers Superior Efficacy In Mouse Models Of Autoimmunity Journal Of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrh26tawivit60fhmqzwqwwkt V4em Zfkyiihy5ryarg7 I2 Usqp Cau

The Role Of Gut Microbiota And Il 23 Il 17 Pathway In Ankylosing Spondylitis Immunopathogenesis New Insights And Updates Sciencedirect

Immune Response Il 23 Signaling Pathway Pathway Map Primepcr Life Science Bio Rad

The Th17 Immune Response In Renal Inflammation Kidney International
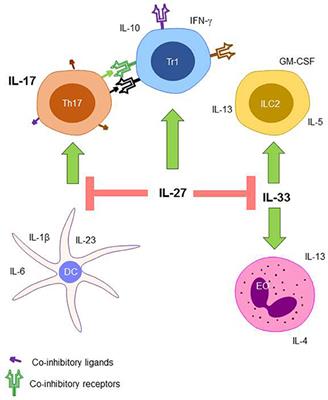
Frontiers Il 17 Il 27 And Il 33 A Novel Axis Linked To Immunological Dysfunction During Sepsis Immunology

The Il 23 Th17 Axis In The Immunopathogenesis Of Psoriasis Sciencedirect
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqjzt7al7gusasabg0wz5h5jckgfmwrvko8gwjobd8i4kur K2w Usqp Cau

Full Text Interleukin 17 And Type 17 Helper T Cells In Cancer Management And Res Itt
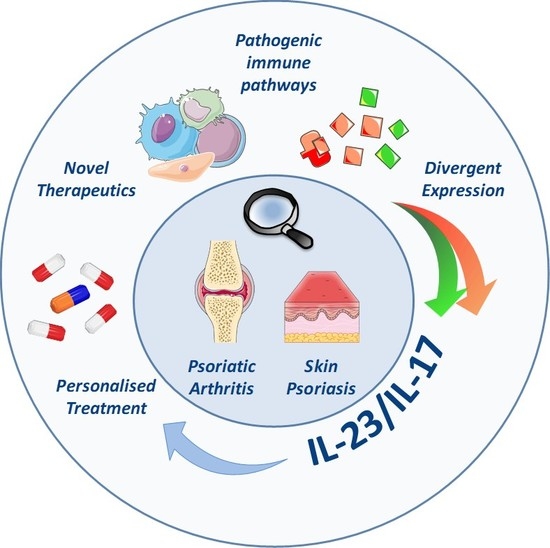
Ijms Free Full Text Role Of The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis The Clinical Importance Of Its Divergence In Skin And Joints Html

Protumor Vs Antitumor Functions Of Il 17 The Journal Of Immunology

Stat3 And Nf Kb Signal Pathway Is Required For Il 23 Mediated Il 17 Production In Spontaneous Arthritis Animal Model Il 1 Receptor Antagonist Deficient Mice The Journal Of Immunology

Il 17 And Th17 Cells In Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis And Vascular Biology

The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Acute Tuberculosis 1 When Inflammatory Download Scientific Diagram

Dual Inhibition Of Interleukin 23 And Interleukin 17 Offers Superior Efficacy In Mouse Models Of Autoimmunity Journal Of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics
Gale Academic Onefile Document The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Inflammatory Arthritis

The Il 23 To Il 17 Cascade In Inflammation And Cancer Adenoma Cells Download Scientific Diagram

A Balance Of Interleukin 12 And 23 In Cancer Trends In Immunology

Targeting The Il 17 Il 23 Axis In Chronic Inflammatory Immune Mediated Diseases Sciencedirect
Www Mdpi Com 1422 0067 19 2 530 Pdf

Il 36 Signaling Facilitates Activation Of The Nlrp3 Inflammasome And Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Renal Inflammation And Fibrosis American Society Of Nephrology

Novel Pharmacological Approaches For Inflammatory Bowel Disease Targeting Key Intracellular Pathways And The Il 23 Il 17 Axis
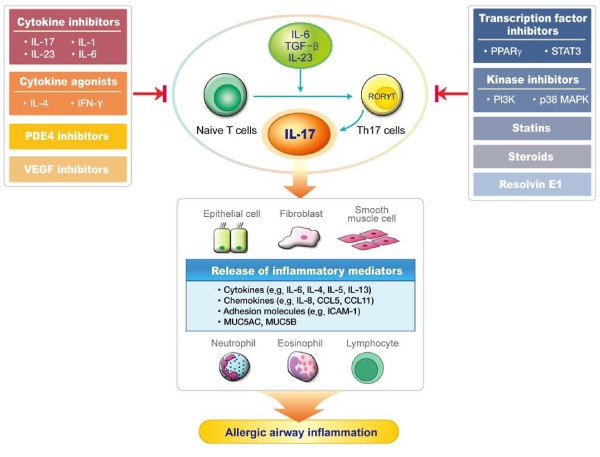
Interleukin 17 Regulation An Attractive Therapeutic Approach For Asthma Respiratory Research Full Text
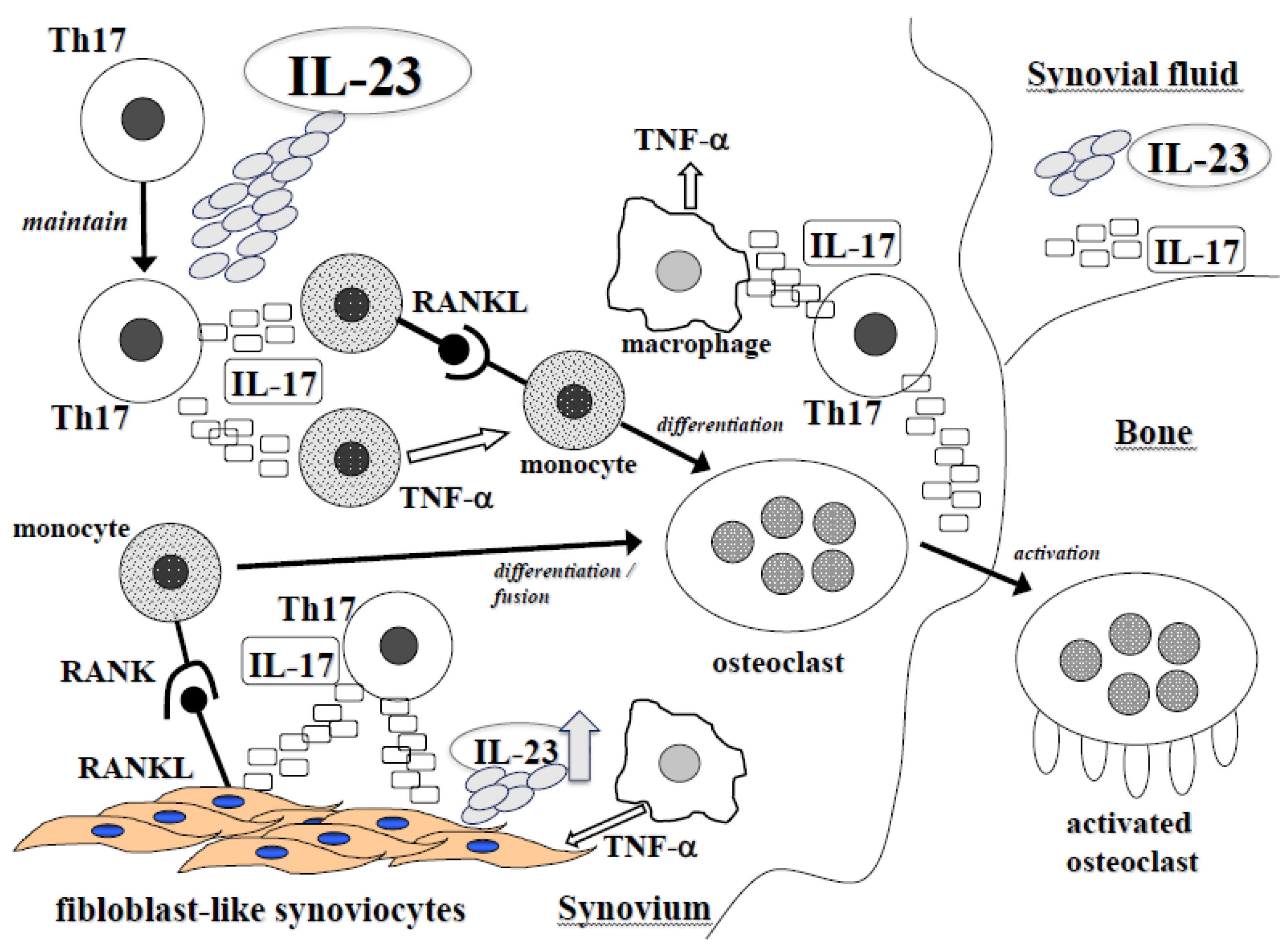
Jcm Free Full Text Il 23 And Th17 Disease In Inflammatory Arthritis Html
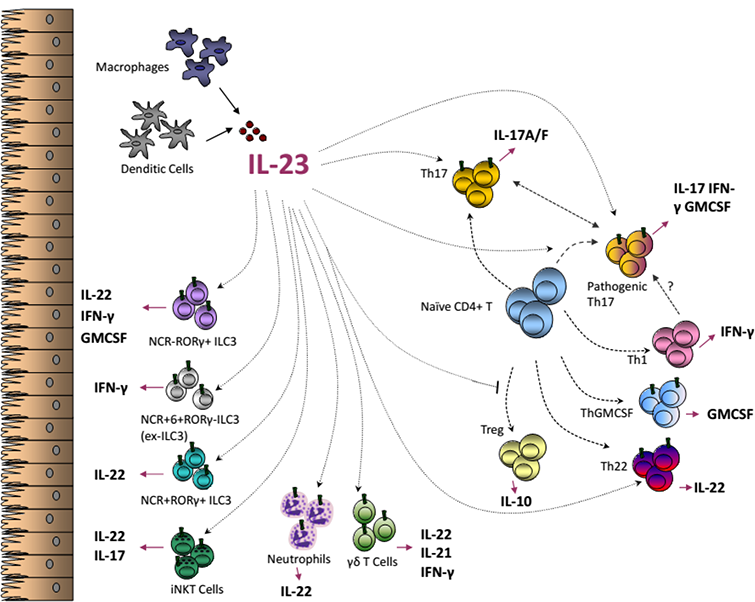
Interleukin 23 In Ibd Pathogenesis Intechopen
Www Jci Org Articles View Version 1 Pdf Render Pdf

Schematic Model Of Il 23 Il 17 Inflammatory Pathway In Ischemic Brain Download Scientific Diagram

The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis And The Role Of Treg Th17 Cells In Rheumatoid Arthritis And Joint Destruction Oa Arthritis

Il 23 Inhibition In Psoriasis A Novel Approach To Convenient Consistent Clearance European Medical Journal

Discovery Of The Il 23 Il 17 Signaling Pathway And The Treatment Of Psoriasis The Journal Of Immunology

Figure 1 Th17 Associated Cytokines As A Therapeutic Target For Steroid Insensitive Asthma
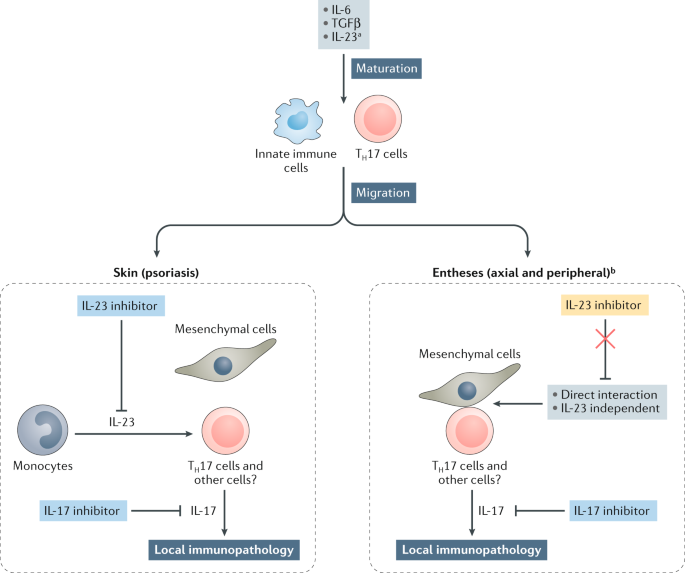
The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway As A Therapeutic Target In Axial Spondyloarthritis Nature Reviews Rheumatology

Interleukin 23 And Interleukin 17 Importance In Pathogenesis And Therapy Of Psoriasis

Efficacy And Safety Of Biologics Targeting Il 17 And Il 23 In The Treatment Of Moderate To Severe Plaque Psoriasis A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Of Randomized Controlled Trials Sciencedirect

Stat3 And Nf Kb Signal Pathway Is Required For Il 23 Mediated Il 17 Production In Spontaneous Arthritis Animal Model Il 1 Receptor Antagonist Deficient Mice The Journal Of Immunology
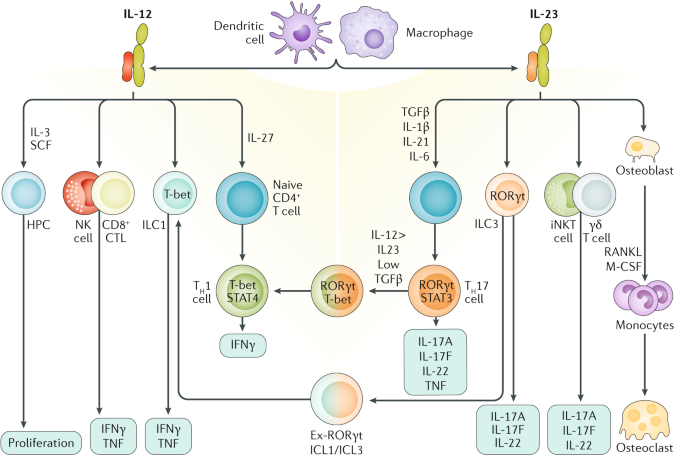
Il 12 Il 23 And Il 17 In Ibd Immunobiology And Therapeutic Targeting Nature Reviews Gastroenterology Hepatology

Interleukin 23 In Psoriasis Integrating New Therapies In The Current Treatment Landscape European Medical Journal



